Symmetric Matrix Diagonalizable
Assume A Q D QT with Q q 1. Then AQ Q D.

Lecture 16 Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors Last Time Matrices
We are now ready to prove our main theorem.

Symmetric matrix diagonalizable. A UDU 1 with Uorthogonal and Ddiagonal. A is diagonalizable because it is an anti-diagonal matrix. Real symmetric matrices not only have real eigenvalues they are always diagonalizable.
The one that is useful here is. -2 5 Find the eigenvalues of the symmetric matrix. A is a symmetric matrix if AT A Definition.
Symmetric matrix A meaning A AT. In other words a basis is orthonormal if eachbasis elementhas unitlength kvik2 vivi 1 for each i and distinct basis elements are. Two vectors u and v in Rn are orthogonal to each other if uv 0 or equivalently if uTv 0.
A matrix A in MnR is called orthogonal if. A matrix P is said to be orthonormal if. We say that U in mathbbRntimes n is orthogonal if UmathsfTU UUmathsfT I_n.
A matrix A 2Rn is symmetric if and only if there exists a diagonal matrix D 2Rn and an orthogonal matrix Q so that A Q D QT Q 0 B B B 1 C C C A QT. Q n q 1. Also the set of eigenvectors of such matrices can always be chosen as orthonormal.
Ie given a real symmetric matrix is diagonal for some orthogonal matrix. Wemake a stronger denition. Of course symmetric matrices are much more special than just being normal and indeed the argument above does not prove the stronger result that symmetric matrices are orthogonaly diagonalizable.
22 Diagonalizability of symmetric matrices The main theorem of this section is that every real symmetric matrix is not only diagonalizable but orthogonally diagonalizable. Assuming that dim E_lambdaA is equal to the multiplicity of lambda for each distinct eigenvalue lambdatext we find a basis for E_lambdaAtext. The zero matrix 0 has that property so it is a symmetric matrix.
It is a beautiful story which carries the beautiful name the spectral theorem. Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices. A matrix is diagonalizable iff it is similar to a diagonal matrix.
If the matrix A is symmetric then its eigenvalues are all real TH 86 p. Real symmetric matrices are diagonalizable by orthogonal matrices. Recall that by our denition a matrixAis diagonal-izable if and only if there is an invertible matrixPsuchthatAP DP1whereDis a diagonal matrix.
There exists an orthogonal matrix P such that P1AP D where D is diagonal. D n d 1 q 1. Diagonalization of symmetric matrices Theorem.
85 Diagonalization of symmetric matrices Definition. More generally matrices are diagonalizable by unitary matrices if and only if they are normal. This is sometimes written as u v.
Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. 366 eigenvectors corresponding to distinct eigenvalues are orthogonal TH 87p. Let A be a square matrix of size n.
The procedure for diagonalizing a matrix is as follows. 369 EXAMPLE 1 Orthogonally diagonalize A 12 21. In fact more can be said about the diagonalization.
2 Ais orthogonally diagonalizable. In other words there is a complex orthogonal rather than unitary matrix of eigenvectors. A PDPT where P.
The set of eigenvalues of a matrix is sometimescalled the spectrum of the matrix and orthogonal diagonalization of a matrix E factors Ein away that displays all the eigenvalues and their multiplicities. Q n orthogonal and D diagd 1. Therefore the theorem is called theSpectral Theorem for real symmetric matrices.
A is diagonalizable because it is a symmetric matrix. Of course the result shows that every normal matrix is diagonalizable. The diagonalization procedure is essentially the same as outlined in Sec.
-12 Points DETAILS LARLINALGSM 73016. A matrix P is said to be orthogonal if its columns are mutually orthogonal. Diagonalization of Symmetric Real Matrices from Handout Definition 1 Let δij 1 if i j 0 if i 6 j A basis V v1vn of Rn is orthonormal if vi vj δij.
Symmetric and hermitian matrices which arise in many applications enjoy the property of always being diagonalizable. Equivalently the matrix is equal to its transpose A A T. A real matrix Ais symmetric if and only if Acan be diagonalized by an orthogonal matrix ie.
366 A is orthogonally diagonalizable ie. Symmetric matrix is similar to a diagonal matrix in avery special way. If Ais an n nsym-metric matrix then 1All eigenvalues of Aare real.
D n q n. Q n diagd 1. At any rate a complex symmetric matrix M is diagonalizable if and only if its eigenvector matrix A can be chosen so that A T M A D and A T A I where D is the diagonal matrix of eigenvalues.
A square matrix A a i j is a symmetric matrix if its entries opposite the main diagonal are the same that is if a i j a j i for all i and j. Theorem 1 The spectral theorem. 53 as we will see in our examples.

Proof For Why Symmetric Matrices Are Only Orthogonally Diagonalizable Mathematics Stack Exchange

Chapter 7 Symmetric Matrices And Quadratic Forms Flashcards Quizlet
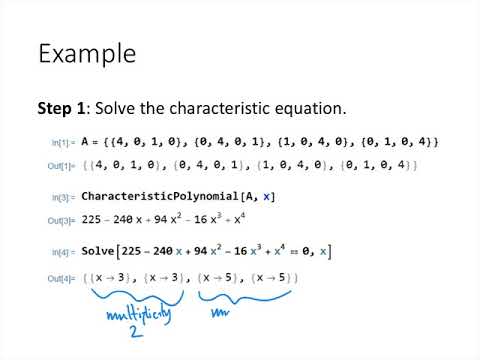
Linear Algebra Lecture 41 Diagonalization Of Symmetric Matrices Youtube

Proof For Why Symmetric Matrices Are Only Orthogonally Diagonalizable Mathematics Stack Exchange
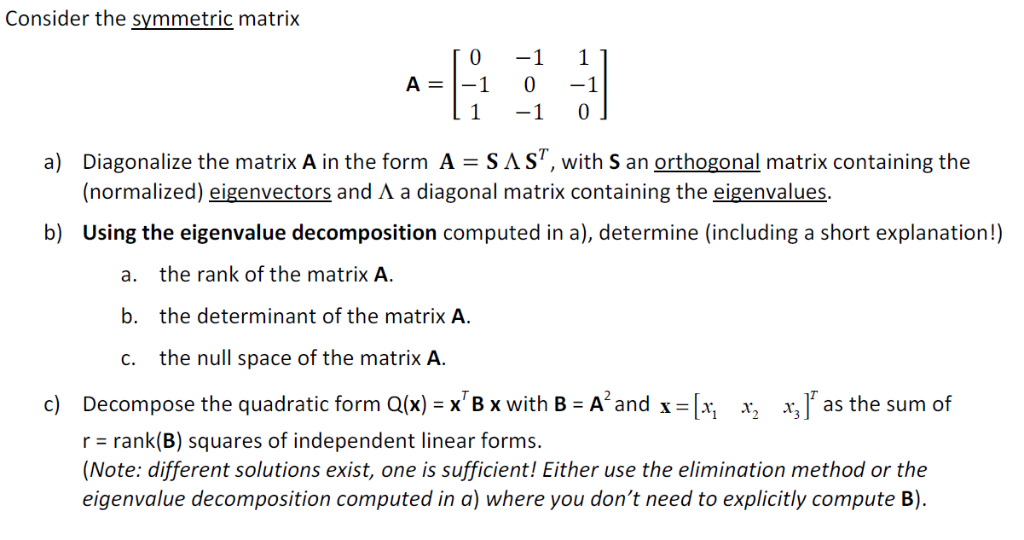
Consider The Symmetric Matrix 1 A 1 1 0 1 1 Chegg Com

Diagonalization Of Symmetric Matrices What Is A Symmetric Matrix What Is An Orthogonal Matrix Youtube

Linear Transformation Standard Matrix The Standard Basis Logic Math Mathematics Math

7 Symmetric Matrices And Quadratic Forms 7 1
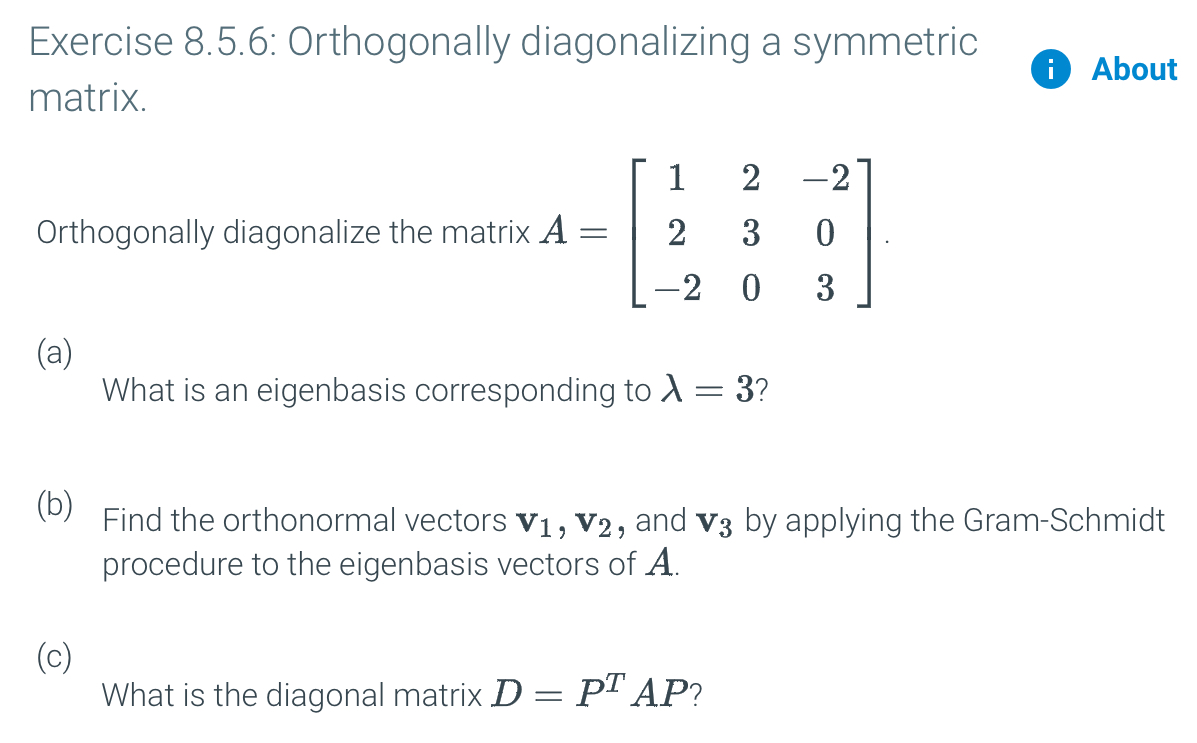
Solved Exercise 8 5 6 Orthogonally Diagonalizing A Symme Chegg Com
Https Www Ucl Ac Uk Ucahmdl Lessonplans Lesson14 Pdf

The Deep Trench Of Mathematics Coolguides Mathematics Infographic Graphic Design Lessons

Symmetric Matrix Don T Memorise Youtube
Http Www Math Odu Edu Bogacki Math316 Transp 8 3 Pdf
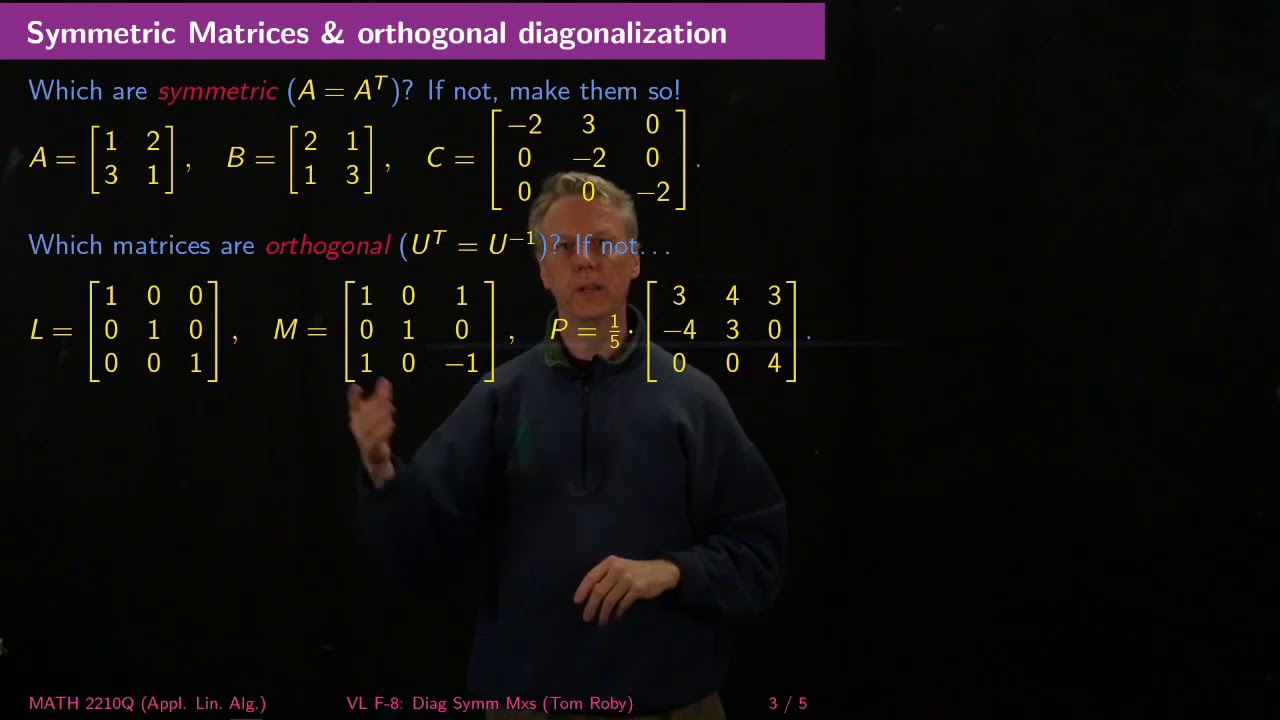
Diagonalization Of Real Symmetric Matrices Linear Algebra F8 Youtube



