How To Calculate Matrix Size In Mri
In MRI the resolution is determined by the number of pixels in a specified FOV. Substitution of zeroes for unmeasured data points in order to increase the matrix size of the new data prior to Fourier transformation of MR data.

Mr Image Quality Frcr Physics Notes
As an example after a T1 tse sequence with 100 FOV 4mm slice thickness 256x256 matrix size and a relative SNR of 100 sees an increase in the matrix size from 256X256 to 320X320 the SNR will reduce to 74.
How to calculate matrix size in mri. Increasing the matrix reduces the voxel size reducing the amount of signal received by the individual pixels. Frequency256 Phase192 FOV200 200256 Frequency direction 200192Phase direction This would create a pixel with 78mm x. FOV 320 Matrix 320 320 voxel size is 3203201mm.
Dividing the field of view by the matrix size gives you the in-plane voxel size. The larger our image matrix is the more pixels we will have in our image. The smaller the pixel size the greater the image spatial resolution.
FOV Matrix pixel size FOV phase matrix phase dimension pixel FOV frequency matrix frequency pixel Convert 20cm to 200 mm before calculating. Pixel size can be calculated by dividing the field of view by the matrix size egFOV 320 Matrix 320x320 Pixel size 3203201mm. Basic resolution and phase resolution.
The five determinants of pixelvoxel dimensions in an MRI examination are. If there is a decrease in FOVpixel size decrease. Pixel size can be calculated by dividing the field of view by the matrix size egFOV 320.
The matrix used in MRI determines the scan resolution. The horizontal lines in matrices are called rows and the vertical lines are called columns. Slice thicknesses in clinical MRI.
There are two resolution parameters used in MRI for the pro-duction of a 2D image ie. We can calculate the size of our pixel by taking the field of view FOV and dividing it by the frequencyphase value. Slice thickness ST Field of view along the phase encode direction FOVp Field of view along the frequency encode direction FOVf Number of phase encoding steps Np This is your phase matrix Number of frequency encoding steps Nf This is your frequency or read matrix.
Multiply phase pixel size by frequency pixel size pixel area squared Frequency dimension of a pixel FOV frequency matrix. For a fixed FOV. Its dimensions are given by the pixel together with the thickness of the slice the measurement along the third axis.
Terms in this set relationship between pixel size FOVfield of view and matrix size. For a fixed matrix. MRI image quality is.
Pixel size FOVfrequencyphase value Example. Pixel sizes range in clinical MRI from mm eg 1 3 1 mm2 to sub-mm. The pixel size is equal to the field of view divided by the matrix size.
200 224 089mm phase dimension 200 256 078mm frequency dimension. A voxel is the volume element defined in 3D space. Orient1 vectorImageOrientationPatient0 ImageOrientationPatient1 ImageOrientationPatient2 orient2 vectorImageOrientationPatient3 ImageOrientationPatient4 ImageOrientationPatient5 orient3 orient1 x orient2 cross product orient_matrix matrixorient1 orient2 orient3 pos1 vectorImagePositionPatient0 ImagePositionPatient1.
El size can be calculated by dividing the FOV by the matrix size eg. Pixel size is typically between 05 and 15 mm. Given along two axes in mm dictating in-plane spatial resolution.
There are two resolution parameters used in MRI for the production of a two dimensional image ie. Pixel size is dependent on both the field of view and the image matrix. Smaller pixels will receive less signal and produce a low SNR image.
The size of our field of view and number of phase and frequency encoding steps will determine our image resolution. Hence increasing the field of view in either direction increases the size of the voxels and decreases the resolution. SNR is directly proportional to voxel size assuming that the number of phase-encoding steps is.
A matrix is an array of numbers in rows and columns. If our field of view is fixed and we increase our image matrix we will make the size of our pixels smaller as they squeeze into the fixed field of view. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m-by-n matrix or m n matrix and m and n are called its dimensions.
Relationship between pixel size FOV and matrix size. The pixel size FOVmatrix determines the in-plane resolution. The field of view is the size of the area that the matrix of phase and frequency encoding cover.
Basic resolution phase resolution Abstract Background. Decreasing the field of view improves the resolution. The matrix size is typically 128x 256x or 512x.
This can be equivalent to performing an interpolation ZIP - zero fill interpolation processing in the transformed data resulting in pixels smaller than the actual resolution of the image. If there is an increased in FOVpixel size increases. Reducing the FOV increasing the matrix number or reducing the slice thickness results in an image with reduced voxel volume.
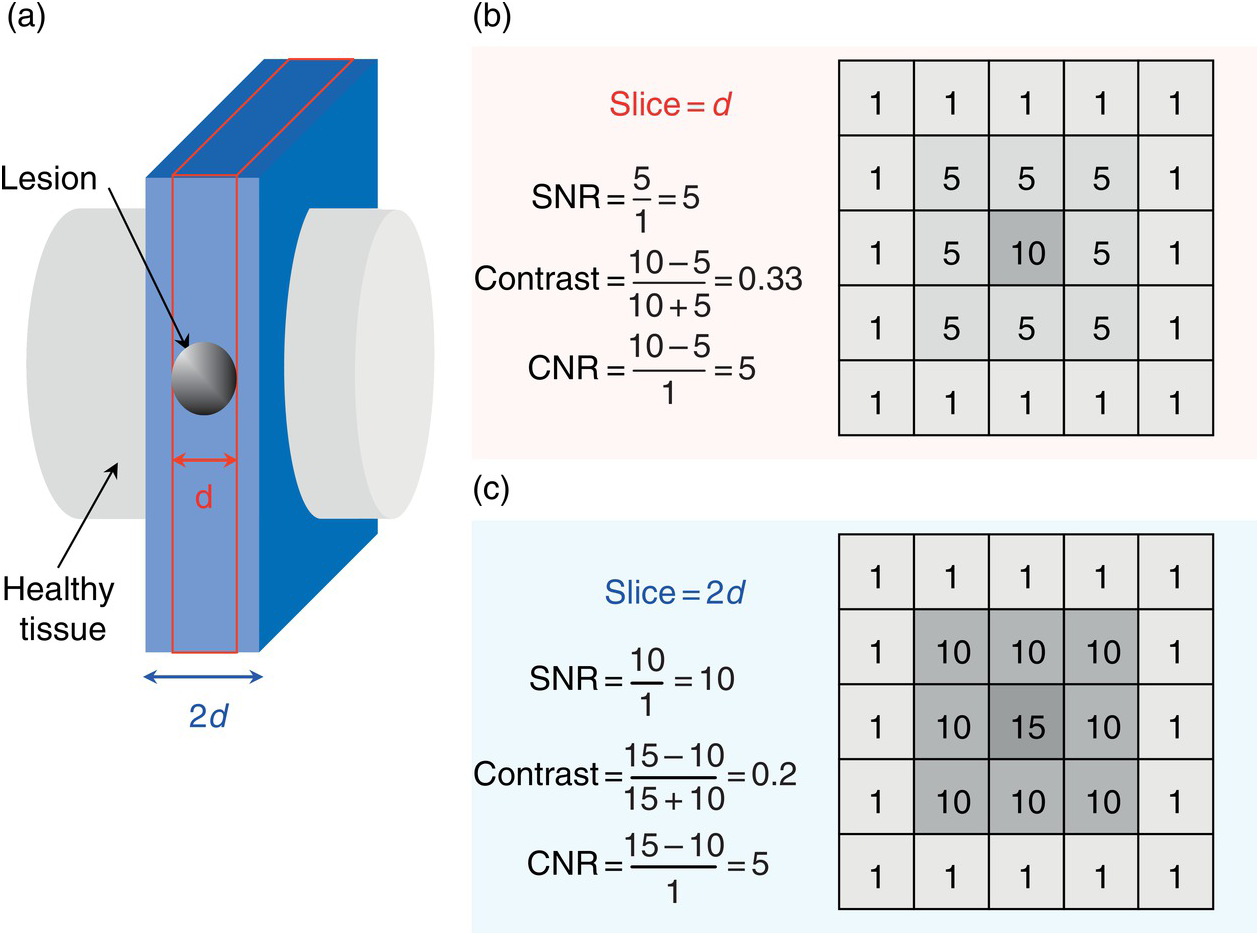
What You Set Is What You Get Basic Image Optimization Chapter 6 Mri From Picture To Proton

Mri Resolution And Image Quality How To Manipulate Mri Scan Parameters

Nipype Beginner S Guide All You Need To Know To Become An Expert In Nipype

Mri Resolution And Image Quality How To Manipulate Mri Scan Parameters

Mri Resolution And Image Quality How To Manipulate Mri Scan Parameters

Mri Resolution And Image Quality How To Manipulate Mri Scan Parameters

Mri Resolution And Image Quality How To Manipulate Mri Scan Parameters

Mr Image Quality Frcr Physics Notes

Mri Resolution And Image Quality How To Manipulate Mri Scan Parameters

Signal To Noise Ratio Snr In Mri Factors Affecting Snr Calculating Snr Mri

Screen Shot 2021 04 01 At 10 15 47 Pm In 2021 Learning Process Deep Learning Learning

Mr Image Quality Frcr Physics Notes
